Kee Safety Fall Protection Experts perform a critical analysis of the entire rooftop surface to identify the hazards where workers are exposed to the greatest risk. This ensures that the most dangerous areas are protected immediately with state-of-the-art fall protection systems and OSHA compliant solutions.
We Assess Risk Based on 2 Factors:
 |
Severity of Injury: In fall protection assessment, the severity of a fall-related injury is always assumed to be life-threatening. |
 |
Likelihood: The greatest predictor for the likelihood of an accident occuring is to review the frequency of exposure to the hazard on the roof. |
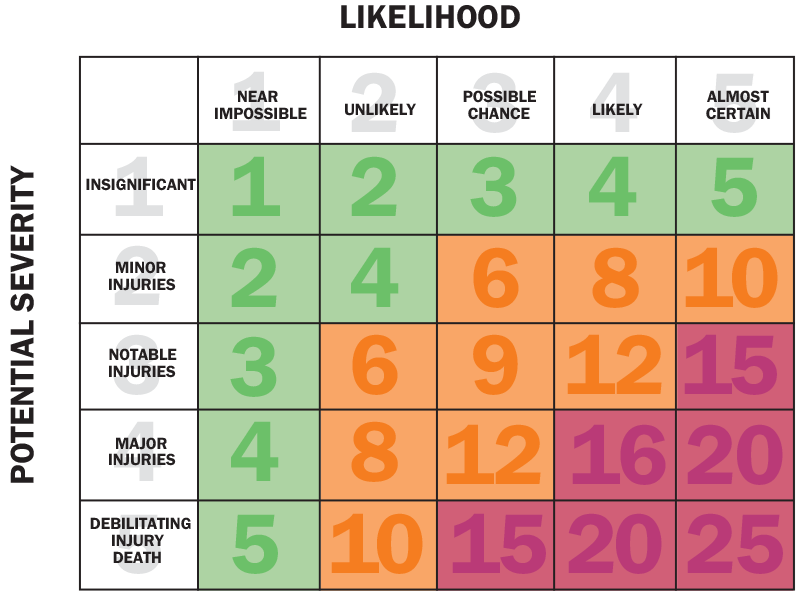
Risk = Severity X Likelihood
We prioritize our Risk Assessment based on the critical danger and how frequently workers are exposed.
The Risk Assessment Matrix

We Identify Danger Zones on Your Roof
Outlined below is our basic approach. Your roof must be reviewed with one of our Kee Safety professionals as each site is unique and your specific roof may require variable solutions.

Access points are the most frequented hazard on any rooftop. Workers are exposed to this risk twice - every time they enter and exit the roof to perform tasks. If a worker is required to access the roof 8 times per year, they are exposed to the access point hazard 16 times. OSHA requires that all ladders and hatches be secured with a self- closing gate and safety-compliant railing.

Openings are the most often overlooked hazard, so they are extremely critical to protect. OSHA considers skylights to be a hole in the rooftop which is why Kee Safety evaluates all rooftop openings as a serious risk concern. Statistically, more people fall through skylights than over the open edge of a roof.
As a worker is traversing the middle of the rooftop, they have a false sense of security. Operating far from the roof edge, carrying equipment, or focused on the job at hand, it is easy to misstep and fall through an unprotected skylight opening.

The edge of the roof is the most visible hazard, and typically the hazard most people want to protect first. Proximity to the roof edge is a significant factor in identifying the likelihood of an accident occurring. OSHA regulations cite that any building where work is performed within 15’ of an open roof edge, each worker must be protected from falling with a guardrail system or other approved safety system. Frequently, a worker’s purpose for accessing the roof is to service a piece of equipment. It is important to document if the equipment too close to an unprotected edge.

Understanding the path that workers take across the roof is necessary for a complete fall protection assessment. Obstacles on the roof force workers to unsafely climb over or step around the obstructions, often placing workers at risk by walking too close to the roof edge and slipping off.



